Hey loves,
Have you ever struggled to stick to a workout despite logically or mentally knowing how beneficial it can be?
Let us discuss the basal ganglia, also known as the brain’s habit engine that literally controls whether you stick to your workouts or not.
By understanding this tiny brain structure, you can train your habits like your muscles. So what is the basal ganglia?
Basal Ganglia 101

The basal ganglia is an important part of the brain responsible for movement, habit formation, reward loops, and habit automation.
This group of nuclei are located deep within the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. They are subcortical, meaning they lie below the outer layer of the brain (aka: the cortex).
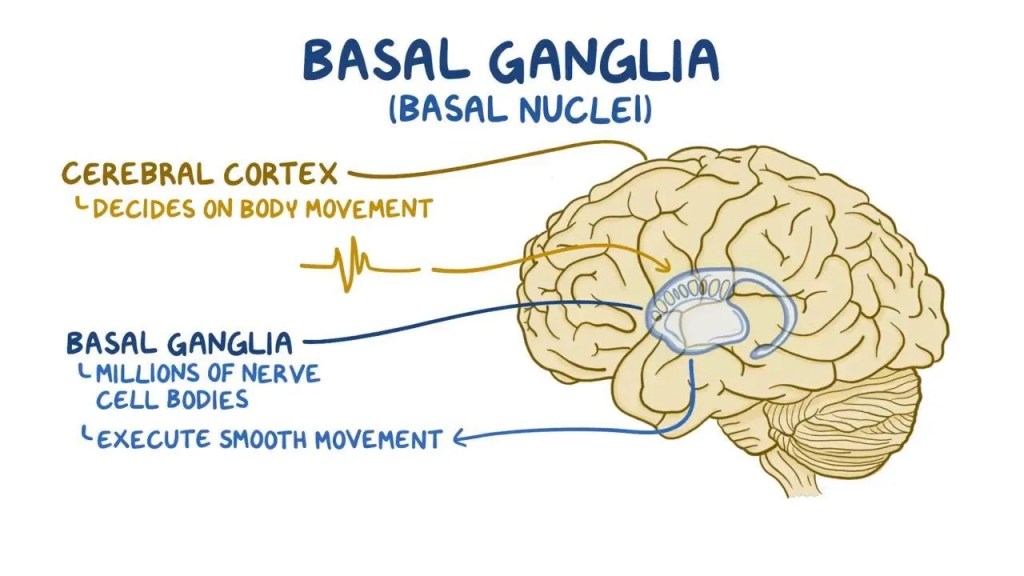
The basal ganglia link your thinking brain, muscles, and reward system. They fine-tune movement while sending signals that make every rep feel rewarding.
Consistent strength and explosive training train your body and your brain, turning effort into habit and motivation.
On the other hand, sedentary behavior and inconsistent workouts can actually weaken these circuits and inadvertently cause less motivation, lack of adherence to habits (even the good ones!) and issues with movement and mobility.
Exercise and Neural Circuitry
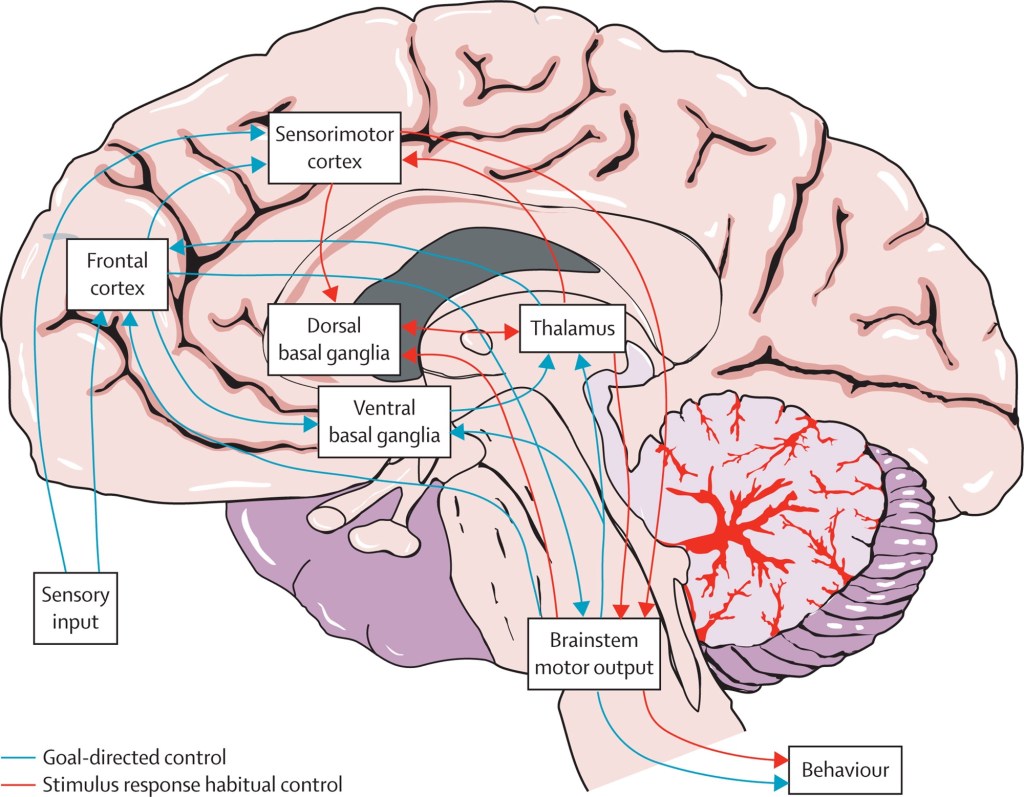
Resistance training, explosive lifts, and fast-twitch fiber recruitment strengthen the basal ganglia pathways.
The more movement and repetition this part of the brain can process and facilitate, the more habits you can eventually adopt.
Interestingly enough, the concept of neuroplasticity (rewiring the brain) can also be applied to the basal ganglia, showing just how intelligent, adaptable and flexible the human body (including the brain) can truly be.
Building Unstoppable Habits

Here are 5 ways to structure workouts to reinforce basal ganglia pathways:
1) Aim for Progressive overload: you should essentially aim to get stronger week in and week out via adding more sets, reps or intensity. Check out this post to know more about to apply this principle!
2) Include explosive movements in your workouts. This includes jump squats, kettlebell swings and explosive hip thrusts.

3) Remain consistent and try to use a variety of different stimuli while sticking to the same lifts over time.
For instance, add bands to deadlifts or try different angles for variety while sticking to the same lifts.
4) I wrote about this one in my previous post on motivation. Habit stacking describes linking exercise to small wins, journaling, or morning routines. This will make it easier for you to stick to your new exercise habit!
To prevent habit decay, I recommend adding novelty and more challenge every 2–3 weeks. This can effectively also break plateaus and allow you to keep seeing better results.
Mental Health Benefits

A strong basal ganglia mixed in with repeated exercise habits improves your overall focus, motivation and stress resilience.
A strong basal ganglia will allow you to overcome procrastination, to keep building consistent routines and as a result, while lowering your anxiety levels.
The benefits of having an active and healthy brain always outweighs the effect of a sedentary lifestyle on our body’s important organ.
It is therefore imperative that we work that muscle, strengthen it at all costs so that it can eventually sustain us longer.
Advanced Insights

Here are a few important concepts on the topic of the basal ganglia and our quest towards optimal mental health via exercise:
Striatal neurons:
These neurons in your brain’s reward center help control movement, motivation, and habit formation.
You can literally use workouts to train your brain to crave progress and consistency. Imagine what this insight can do to you when you doubt the effectiveness of exercise!
Dopamine receptor modulation:
Simply adjusting how your dopamine (motivation) receptors respond affects how motivated and rewarded you feel; lifting weights and hitting fitness goals naturally fine-tunes this system for long-term drive.
Every time you lift, you invest in your long-term potential via the process of motivation.
3. Glutamate interactions:
Glutamate is a key messenger in your brain that works with dopamine to strengthen neural pathways. Basically, it helps your brain lock in habits, focus, and muscle memory from training.
In conclusion, I encourage you, my readers, to treat your workouts like brain training and not just muscle building.
Every part of your body is intelligent so don’t let your brain’s mechanisms go to waste, invest in your longevity at all costs!
I hope that you enjoyed this blog post on How Your Basal Ganglia Builds Unstoppable Exercise Habits, please let me know what you thought about it in the comments section below!

One Comment Add yours